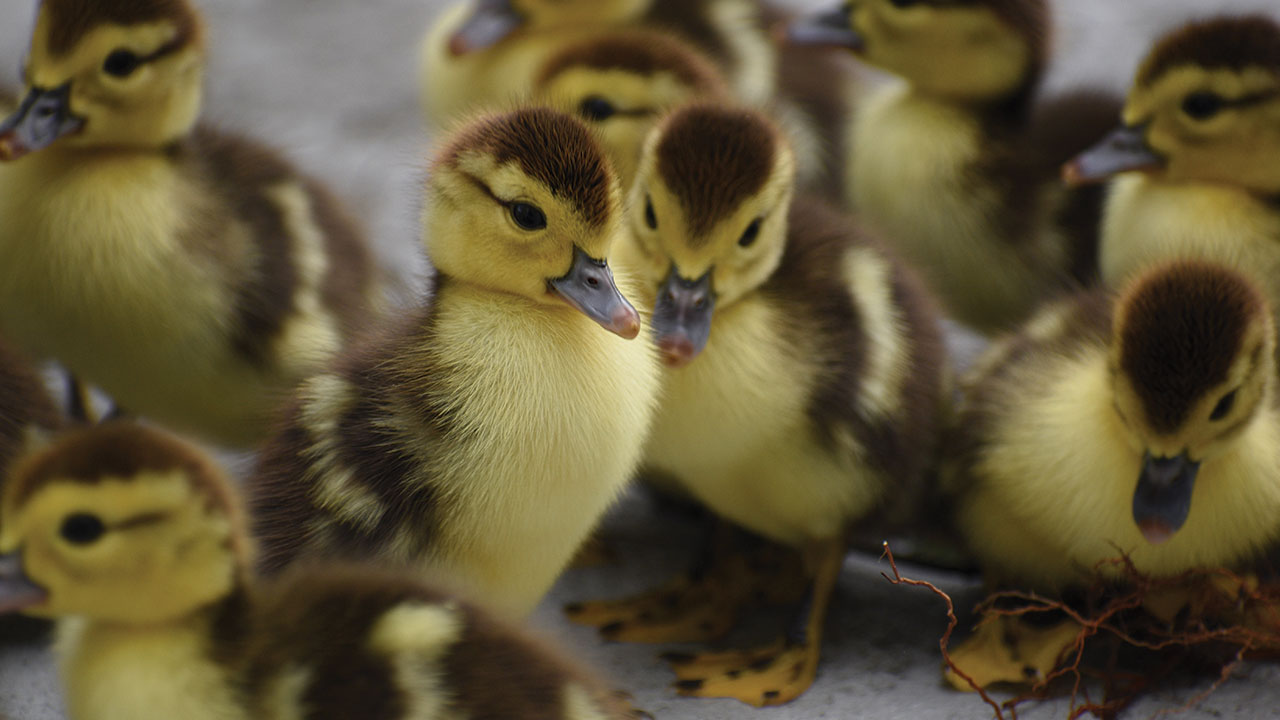
We recently wrote a guide on how to hatch duck eggs, but not all breeds of duck are the same! Incubating Muscovy duck eggs is a little bit different, and the differences involved I think are worth writing a separate piece on. If you’re getting ready to hatch your own Muscovy duck eggs, you should be prepared for a bit longer of a wait for them to hatch. The wait can be grueling, but what your new baby ducks hatch out, it’s so worth it! So let’s dive right in.
If you’re just getting started and need an incubator, I strongly recommend the Manna Pro Harris Farms Nurture Right Incubator. This is an incubator I personally use for hatching eggs. It has an automatic egg turner suitable for 22 duck eggs and a full 360-degree view, which is awesome when the eggs start to hatch. If you are looking to hatch more eggs than that, the Hatching Time Cabinet Incubator is pretty much unbeatable. You can incubate as many as 80 duck eggs in this incubator.
Incubating Muscovy Duck Eggs – The Basics
When it comes to incubating Muscovy duck eggs, you really have to get the basics right. If even one setting is off, it can lead to a poor hatch, or even worse, no ducklings at all! So let’s talk about the very basic stuff you need to know about hatching your own Muscovy ducklings.
- Incubation time: 33-37 days
- Incubator temperature: 37.5°C (99.5°F)
- Incubator humidity: 55% or 84.5°F if you use a wet bulb thermometer
- Egg turning: 4 times a day
- Candling eggs: Day 7
- Lockdown Date: Day 30
- Lockdown temperature: 37.2°C (99°F)
- Lockdown humidity: 65% or 88°F if you use a wet bulb thermometer
Incubating muscovy duck eggs is an exercise in extreme patience. Most breeds of duck will hatch after about 28 days, but the Muscovy duck can take up to 37 days. Your eggs will need to be consistently incubated at 37.5°C (99.5°F) up until 4 days before hatching. During the final 4 days of incubation, the temperature is reduced slightly and the humidity is increased. You also stop turning the eggs at this point.
Candling your Muscovy duck eggs on the 10th day of incubation is an important part of the process. It will help you determine whether or not your eggs are viable and allows you to discard non-viable eggs before they become a health risk. More on that later.
How to hatch duck eggs
I’ve hatched dozens of batches of eggs in my life. There is some advice online that is spot on and some that is not. Be cautious of reading forums where people discuss egg hatching tips. It really boils down to making sure your fundamentals are rock solid and being patient – allowing nature to take its course. In this section of the article, we’ll go over everything (and I mean everything!) that you need to know about incubating duck eggs successfully.
The anatomy of an egg
Nature knows how to hatch an egg. By providing the basic needs of an egg, heat and humidity, it will likely eventually hatch. But knowing the anatomy of a duck egg is important for getting a good hatch rate. The three parts of the egg that you should be very familiar with are the shell, the yolk, and the air sac. Below is an image of the anatomy of an egg:
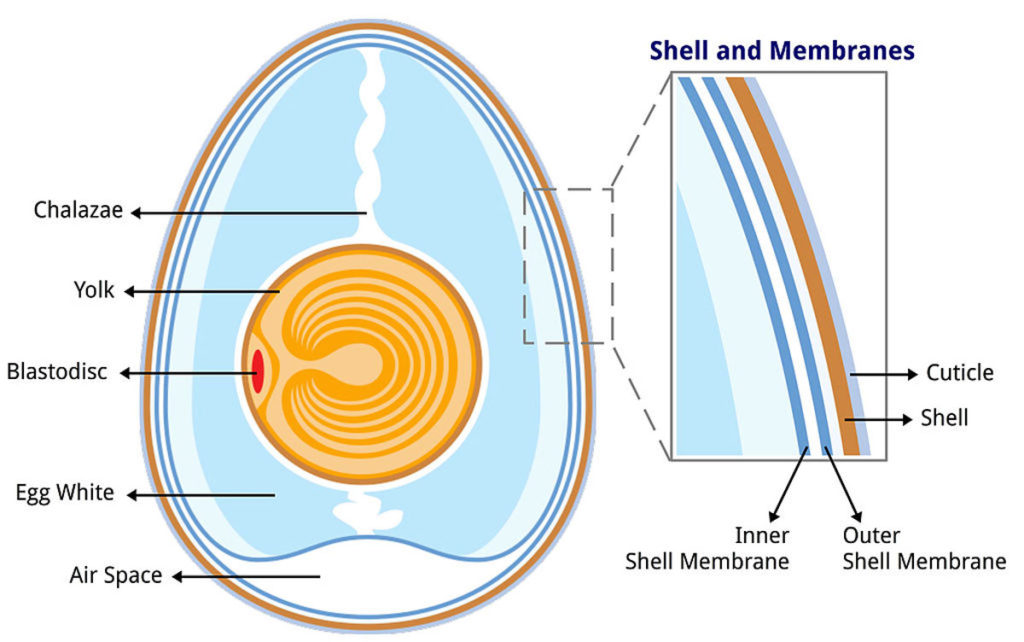
You will need to pay special attention to the quality of the shell, the air space at the fat end of the egg, and the yolk suspended inside of the egg.
Selecting quality duck eggs to hatch
How do you select a quality duck egg to hatch? Where do you get fertile duck eggs? Can you just incubate duck eggs from the local market? Picking the right duck eggs to hatch is the first and probably most important step in incubating eggs. Don’t try to incubate supermarket eggs – they probably won’t hatch. Instead, look for a local, trusted seller of fertilized eggs. Find a farm that will allow you to see the flock of ducks being bred for eggs. This will ensure that you’re getting what you’re paying for and that the birds are treated well.
You may also purchase fertilized duck eggs from the internet. Many hatcheries will gladly ship eggs to you, but it comes at a price. Shipped eggs are expensive, can arrive damaged, and have a reduced hatch rate built in due to trauma sustained during shipping.
When you have your eggs in hand, carefully examine each egg. Be sure to wash your hands before and after handling the eggs every single time. You may darken a room and candle your eggs by shining a flashlight into the egg. This will reveal any cracks or imperfections inside of the egg.
Never try to incubate an egg that’s cracked, dirty, too large, too small, misshapen, double yolked, or unusual in any way. Also be aware that eggs with a defective air cell should not be incubated. These eggs are likely not viable and will probably not hatch.
Be aware of the rough age of the eggs as well. 7 days after a duck egg is laid, it begins to rapidly lose fertility. Getting your eggs set in the incubator within a week of being laid is vital. After 2-3 weeks, most of your duck eggs won’t be viable anymore.
Letting your eggs settle
Once you’ve picked up your eggs, whether it’s from your local postal office or from a local farm, you’re going to want to allow your eggs a minimum of 12 hours, though ideally more like 24 hours, to settle. Place them in the carton with the fat side of the egg pointed upward. This will allow the air cell at the fat end of the egg to settle into place before incubating.
Your eggs should be given plenty of time to reach room temperature. Putting colder eggs in an incubator can breed bacteria as the egg heats up. Always start incubating Muscovy duck eggs from room temperature.
How to clean an incubator
Before setting eggs in your incubator, it is important to properly clean and sanitize it. Incubators are hot and humid – perfect for bacteria to grow. We want to prevent as much bacterial growth as possible, so a proper cleaning protocol is a must.
- If you have used your incubator before, be sure that any pieces of shell or any other material left over from past hatches has been removed from the incubator.
- Remove all of the removable components, like water pans and egg trays, and clean them with soap, water, and a sponge. After cleaning, you can further disinfect these components by soaking in warm water with a mild bleach. Don’t use chemical cleaners.
- Wipe down each of the components and allow to dry.
- Now, clean the bottom of the incubator by soaking it in a 25% bleach and water solution. Wipe it down with a soft cloth.
- Gently clean the heating unit, but avoid getting it wet. A slightly damp cloth or a brush is the ideal way to clean the heating unit.
Once it’s been cleaned, allow it to sit in a protected spot for 12-24 hours.
Setting up your incubator
Once your incubator has been disinfected, it’s time to get it set up. Never start your incubator and immediately set eggs. It’s not like the lazy way of cooking a frozen pizza in an oven that’s not preheated yet! You want to make sure each of the fundamental aspects of incubating Muscovy duck eggs is spot on. If your temperature is over a few degrees, your eggs will die and you’ll be in for a sad time. If it’s too low, it can impact development negatively. If the humidity is wrong, again, you can have ducklings that don’t develop or hatch properly. Sad times all around.
48 hours before you begin incubating Muscovy duck eggs, set up the incubator and get all of its measurements stabilized. You’ll want to see that the temperature and humidity are stable for at least 12 hours before setting eggs. As a reminder, you will want these two readings to be perfect:
- Incubator temperature: 37.5°C (99.5°F)
- Incubator humidity: 55% or 84.5°F if you use a wet bulb thermometer
Once you are certain that your incubator is stable and ready for eggs, go ahead and set them.
Turning your duck eggs
In the wild, a mother bird sitting on her eggs is always busy rotating and turning her eggs. When incubating duck eggs, or any other type of poultry egg, this action must be simulated by manually turning the eggs or using an automatic egg turner. Automatic egg turners are especially nice because you don’t run the risk of contaminating the inside of the incubator or the eggs themselves by touching them and you don’t run the risk of throwing off the internal temperature and humidity.
If you don’t have an automatic egg turner, it’s not the end of the world. You can turn your eggs by hand. Always wash your hands before touching your eggs! The oils and dirt on your hands can clog the pores in the shell or contaminate the eggs with bacteria. Either scenario can kill them.
If turning manually by hand, before you set them, take a soft pencil and place an X on one side of the egg and an O on the opposite side of the egg. This will help you make sure each egg has been fully turned. You will continue your daily turning of the eggs until 4 days before hatching.
Candling Muscovy duck eggs
Candling the eggs you’ve been incubating is hands down my favorite part of the process. To candle an egg, you darken a room and then shine a flashlight into the large end of the egg. You can cut a hole in a cardboard box to help focus the light, or buy an egg candling light.
If you were to candle your eggs daily, which I do not recommend, you would see a red disk appear on the yolk, followed by veins slowly branching outward. On the 10th day of incubation, you will see a network of veins around the yolk of the egg and a small, red point at the center of it all. You may be able to make out a very dark spot, which is the bird’s developing eye. You may see some movement. If the egg appears alive, congratulations! Go ahead and set it back in the incubator. Below is an image of what a live egg should look like:
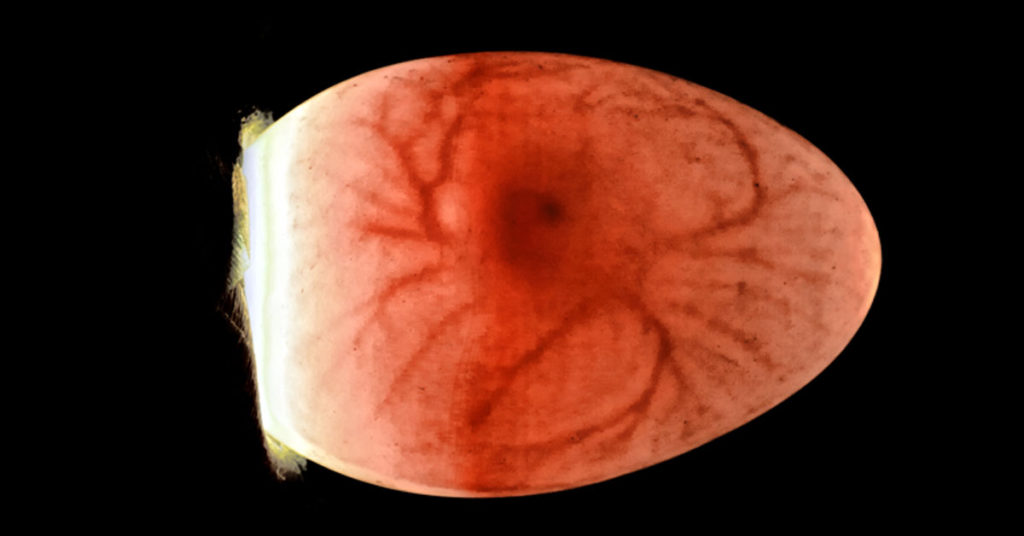
You can clearly see the network of veins, the embryo in the center, and even its eye. At this stage, you might see the embryo rocking back and forth. But there are signs that your egg is not viable:
- Clear, no development at all
- Some early development, but veins have decayed and no new development
- A large red ring with no veins or embryo apparent
- Cloudy, discolored eggs
Any eggs that appear to have died should be discarded immediately. If you are not sure, mark the egg with a question mark and set it for a few more days. Candle again at day 10, but only that egg.
Avoid over-candling. It’s so neat seeing the babies develop, but the more you handle the eggs, the higher the chance that you’ll drop it or infect it with some kind of deadly pathogen.
Monitoring water loss during incubation
Shortly before lockdown, the last 4 days of incubation, I candle the eggs again to look for problems. Any embryos that appear to have died should be removed. I also look at water loss during incubation. Your duck eggs will lose about 14% of the fluid inside the egg as it develops. The air cell at the fat end of the egg should grow some during the incubation process. If it still appears small, your humidity could be too high. If it is very large, it may be too low. Check your hygrometer for an updated humidity reading.
Incubator lockdown
We’ve touched on lockdown a few times in this article. Lockdown is the term given to the last 4 days of incubation. During lockdown, you remove the eggs from the egg turner and lay them on their side, slightly reduce the temperature of the incubator, increase relative humidity, and leave your eggs alone. During this time, the duckling growing inside will get itself into a hatching position and pop out. Fast facts about lockdown:
- Lockdown Date: Day 30
- Lockdown temperature: 37.2°C (99°F)
- Lockdown humidity: 65% or 88°F if you use a wet bulb thermometer
Once your lockdown is initiated, all there is to do is wait.
During these final days of incubation, your ducklings will internally pip. This is the process where your duckling will penetrate the air cell of the egg and begin breathing. 2 days before your ducklings hatch, they will likely externally pip, where they crack the outside of the shell and begin breathing outside air.
During this period, the duckling will begin absorbing the remaining yolk inside of the egg into their bodies. Ducklings are able to survive on this yolk for a day or two after they hatch, at which point they begin to eat and drink.
The general rule of thumb is once you see a pip in the shell, which may appear like a crack or a bump, your duckling should hatch within a day or two. As it prepares to hatch from the egg, it will slowly rotate, breaking the egg shell in a process called unzipping. This is the final stage of hatching. Once they have begun to unzip themselves, hatching is imminent. This part can be difficult for excited duck hatchers. It can be slow, but don’t interfere.
Note: If you get impatient and try to help a duckling hatch, you may accidentally kill it. If the yolk isn’t fully absorbed and you pull the duckling from the shell, this radically increases the odds that the duckling will not survive.
The period of time from pip to zip can vary pretty widely. In my experience, once you see an external pip, the duckling will fully hatch within 24 hours. The eggs may not all hatch at once. Or they might. It really depends on a number of factors that are nearly impossible to account for. I’ve had hatches where every single egg hatches at the exact same time and some where ducklings hatch a few days late. You just have to be patient.
The important thing is to be patient and not mess with the eggs. Hatching eggs can be taxing if you’re emotionally invested. Some eggs won’t pip and hatch. Some will internally pip but not externally pip. Some will externally pip but never unzip. Some will unzip but won’t be able to push out of their shell. Some will fully hatch and then die.
If you think a duckling is struggling to hatch, don’t intervene. It sounds callous, but if a duckling can’t hatch on its own, it means it wasn’t strong enough to do so. Some duckling are also slow hatchers. Intervening too early can kill them. Let nature take its course.
If you help a duckling that can’t hatch on its own, any offspring they have may also be predisposed to having difficulty hatching. This is something to consider if you plan to continue breeding that line of duck,
Incubating Muscovy duck eggs naturally
Incubating Muscovy duck eggs naturally is also a viable option for you if you have a female that’s ready to sit. Not every breed sits on eggs very well. My Khaki Campbell and Pekin ducks are reluctant to sit on their eggs. The Pekin hens will build a nest and lay eggs but don’t quite connect the dots for sitting on them. Muscovy ducks are an excellent breed of duck if you want them hatching their own eggs, but be advised: Muscovy ducks are tough. They will protect their eggs and babies from you, delivering a sometimes surprisingly painful bite.
Common duck egg incubation problems
If you’ve gone through the process of incubating Muscovy duck eggs and didn’t get many – or any – ducklings, I understand that can be a difficult thing to experience. You’ve been incubating your eggs for likely about a month and have little to show for it. Now we troubleshoot. What are the more common causes of poor hatch rates?
- Setting old eggs
- Eggs with low fertility
- Improper turning
- Improper handling
- Uneven incubator temperature
- Uneven incubator humidity
- Nutritional deficiencies with the breeding stock (remember when I suggested meeting the birds?)
- Contaminated incubator
We hope this guide for incubating Muscovy duck eggs helps you have a successful hatch!
Other hatching guides:
- How To Incubate Chicken Eggs
- How To Incubate Coturnix Quail Eggs
- How To Incubate Bobwhite Quail Eggs
- How To Incubate Duck Eggs
- How To Incubate Turkey Eggs
- How To Incubate Goose Eggs
- How To Incubate Chukar Eggs













