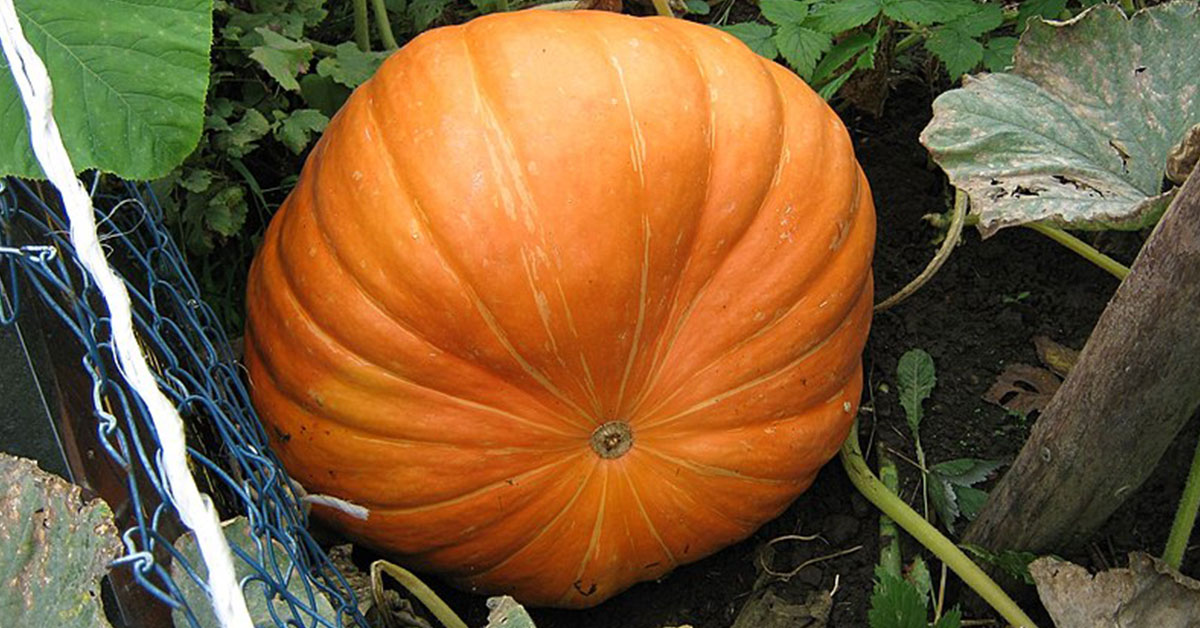
The Atlantic Giant pumpkin is a fascinating variety of pumpkin that has captivated the attention of gardeners and pumpkin enthusiasts around the world. This particular type of pumpkin is known for its massive size, with some specimens weighing in at over 1,500 pounds! While the Atlantic Giant pumpkin is often grown for competitions and record-breaking attempts, it is also a popular choice for fall decorations and pumpkin pies. In this blog post, we will explore the history, characteristics, and growing tips for the Atlantic Giant pumpkin.
What is an Atlantic Giant Pumpkin?
The Atlantic Giant Pumpkin is a variety of pumpkin that is known for its enormous size. It is one of the largest pumpkin varieties and can weigh anywhere from 200 to over 1,500 pounds. These pumpkins are typically grown for competition or for display at fall festivals.
The Atlantic Giant Pumpkin is a type of Cucurbita maxima, which is a species of squash. It was first developed in the late 1800s by John Wallace, a Canadian farmer, who crossed several different varieties of pumpkins to create this giant pumpkin. Since then, growers have continued to develop and refine the Atlantic Giant Pumpkin into the impressive size and shape we know today.
To grow an Atlantic Giant Pumpkin, it requires a lot of care and attention. The plants need plenty of space, sunlight, and water, as well as nutrient-rich soil. Growers often use specialized techniques to encourage the pumpkin to grow as large as possible, such as hand pollination, pruning, and selective watering.
Overall, the Atlantic Giant Pumpkin is an impressive and unique variety of pumpkin that is sure to impress anyone who sees it. While it may require a lot of effort to grow, the end result is well worth it for those who love to compete or show off their gardening skills.
How to start Atlantic Giant Pumpkin seeds
Growing pumpkins from seed is an incredibly rewarding and relatively easy gardening endeavor. With the right preparation and care, anyone can experience the joy of watching these vibrant vines produce bountiful, colorful pumpkins. Starting pumpkins from seed allows you to choose from a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and colors to suit your preferences.
Additional Resource: Our Full Guide On Starting Pumpkins From Seed
Growing & care
Caring for pumpkins is remarkably straightforward, making it an ideal choice for both novice and experienced gardeners. Once established, pumpkins require minimal maintenance.
- Transplanting: When the danger of frost has passed and the soil has warmed up, transplant the pumpkin seedlings into your prepared garden bed or large containers. Ensure they are spaced 3-5 feet apart to allow for proper growth and airflow.
- Care and Maintenance: Water your pumpkin plants deeply and regularly, aiming for about 1-2 inches of water per week. Mulch around the plants to conserve moisture and suppress weed growth. Monitor for pests and diseases, and take appropriate action if necessary.
- Pollination: Pumpkins require pollination for fruit set. Bees and other pollinators are crucial for this process. To encourage pollination, avoid using insecticides that could harm pollinators and consider hand-pollinating if necessary.
- Fertilization: As the pumpkin plants grow, provide them with regular feedings of balanced fertilizer according to the package instructions. This will help support healthy foliage growth and fruit development.
- Pruning and Training: Control the growth of your pumpkin vines by gently pruning back excessive foliage. This promotes better airflow and directs energy towards fruit production. Use trellises or supports to train the vines if desired.
- Harvesting: Harvest pumpkins when they reach their full color, have a hard rind, and the stem starts to dry out. Cut the pumpkins carefully from the vine, leaving a few inches of stem attached. Handle them gently to avoid any damage.
Common pumpkin pests and diseases
Growing pumpkins can sometimes encounter a few common problems. Here are some issues you may face and their corresponding solutions:
- Powdery Mildew: This fungal disease appears as a white, powdery coating on the leaves, causing them to wither and die. To combat powdery mildew, ensure proper spacing between plants for good air circulation. Apply fungicides as a preventive measure or use organic treatments like neem oil or a mixture of baking soda and water.
- Squash Bugs: These pests feed on the leaves, causing wilting and stunted growth. Handpick and destroy the bugs or use insecticidal soap to control their population. Placing floating row covers over young plants can prevent squash bugs from laying eggs.
- Vine Borers: The larvae of squash vine borers burrow into the stems, leading to wilting and plant death. Cut open the stem, remove the borer, and mound soil at the base of the affected plant to encourage rooting. Applying row covers early in the season can help prevent adult borers from laying eggs.
- Blossom End Rot: This physiological disorder manifests as sunken, darkened areas on the blossom end of the fruit. It is caused by calcium deficiency or inconsistent watering. Maintain consistent soil moisture levels, provide adequate calcium through organic amendments, and mulch around the plants to regulate soil moisture.
- Poor Fruit Set: Insufficient pollination can result in poor fruit development. Encourage pollinators by planting pollinator-friendly flowers nearby. In the absence of sufficient pollinators, hand-pollinate by transferring pollen from male to female flowers using a small brush or cotton swab.
- Overwatering or Root Rot: Excessive watering or poorly drained soil can lead to root rot and plant decline. Allow the soil to dry slightly between waterings, and improve drainage by amending the soil with organic matter or growing pumpkins in raised beds.
- Weeds: Weeds compete for nutrients, water, and sunlight, hampering pumpkin growth. Regularly weed around the plants to minimize competition and maintain a weed-free zone.
Remember to monitor your plants regularly, catch problems early, and apply appropriate treatments promptly. By implementing these preventive measures and taking swift action when needed, you can address common pumpkin-growing problems and enjoy a successful harvest.
Common problems
When it comes to growing Atlantic Giant pumpkins, there are a few common problems that many gardeners encounter. Here are some of the most common issues, as well as tips for avoiding or addressing them.
- Poor Soil Quality
Atlantic Giant pumpkins require rich, well-draining soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8. If your soil is too sandy or clay-heavy, it may not provide the nutrients that your pumpkin needs to grow. Consider adding compost or other organic matter to your soil to improve its quality. - Lack of Water
Pumpkins are thirsty plants, and Atlantic Giants are no exception. Without sufficient water, your pumpkin may not grow to its full potential. Be sure to water your pumpkin regularly, especially during hot, dry spells. - Pests and Diseases
Like any plant, Atlantic Giant pumpkins are vulnerable to a variety of pests and diseases. Common problems include powdery mildew, squash bugs, and cucumber beetles. To avoid these issues, be sure to keep your garden clean and free of debris, and consider using organic pest control methods. - Improper Pollination
If your pumpkin flowers are not properly pollinated, your pumpkin may not grow to its full potential. To ensure proper pollination, consider hand-pollinating your pumpkin flowers or attracting pollinators to your garden. - Too Much Competition
Atlantic Giant pumpkins require a lot of space to grow, and they don’t like to be crowded. If you’re growing multiple pumpkins in a small space, they may not have enough room to reach their full potential. Consider spacing your pumpkins at least 10 feet apart to give them plenty of room to grow.
By taking these common problems into account and making adjustments as needed, you can increase your chances of growing a healthy, robust Atlantic Giant pumpkin.
When to harvest Atlantic Giant pumpkins
The Atlantic Giant pumpkin is a variety of pumpkin that is known for its massive size and weight. These pumpkins can weigh up to 2000 pounds and can grow up to 2 feet in diameter. Harvesting the Atlantic Giant pumpkin at the right time is crucial to ensure that the pumpkin reaches its full potential.
The ideal time to harvest the Atlantic Giant pumpkin is when the stem begins to dry out and turn brown. This is usually around 120 to 140 days after planting. It is important to note that the pumpkin should not be harvested before this time, as it may not have reached its full size and weight potential.
Another way to determine if the pumpkin is ready for harvest is by checking the skin. The skin should be hard and resistant to scratches and punctures. If the skin is still soft, the pumpkin is not ready for harvest.
When harvesting the Atlantic Giant pumpkin, it is important to use a sharp knife or pruning shears to cut the stem about 4 to 6 inches away from the pumpkin. Leaving a longer stem can increase the risk of the pumpkin rotting at the stem.
After harvesting the pumpkin, it is important to store it in a cool, dry place with good ventilation. This will help to prevent rotting and prolong the life of the pumpkin.
Harvesting the Atlantic Giant pumpkin at the right time is crucial to ensure that it reaches its full potential. By waiting until the stem begins to dry out and turn brown, and checking the skin for hardness, you can be sure that your pumpkin is ready for harvest. Remember to use a sharp knife or pruning shears to cut the stem and store the pumpkin in a cool, dry place with good ventilation.
Uses for Atlantic Giant pumpkins
Atlantic Giant pumpkins are known for their massive size and are often used for competitive pumpkin growing contests. These pumpkins can grow up to 1,500 pounds and have been known to break world records.
Aside from their use in competitions, Atlantic Giant pumpkins are also used for decorative purposes during the fall season. Their large size and unique shape make them perfect for carving and displaying as Halloween decorations.
In addition, the flesh of these pumpkins is often used for cooking and baking. The flesh is sweet and can be used in various recipes, from pumpkin pie to soups and stews. The seeds can also be roasted and eaten as a snack.
Overall, Atlantic Giant pumpkins have a wide range of uses, from decorative to culinary, making them a popular choice among pumpkin enthusiasts.